Unlocking the Green Thumb: Exploring Organic Fertilizer Options for Home Gardens and Small Farmers
In recent years, the popularity of organic gardening and sustainable agriculture has been on the rise. As more people become conscious of the impact of synthetic fertilizers on the environment and their own health, organic fertilizers have emerged as a viable alternative. This blog post aims to shed light on various organic fertilizer options available to home gardeners and small-scale farmers. Additionally, I will emphasize the importance of soil testing to determine fertility levels and ensure optimal plant growth. Let’s dive in!
Compost: Nature’s Black Gold
Compost is often considered the gold standard of organic fertilizers. It is a nutrient-rich blend of decomposed organic matter, such as kitchen scraps, yard waste, and livestock manure. The benefits of compost include improving soil structure, enhancing water retention, promoting beneficial microorganisms, and supplying a balanced range of macro and micronutrients.
Vermicompost: Worms at Work
Vermicompost is compost produced with the help of earthworms. These industrious creatures break down organic waste, creating a nutrient-dense soil amendment. Vermicompost is known for its high levels of beneficial microorganisms, increased nutrient availability, and improved soil aeration. It also aids in pest control and disease suppression.
Manure: Harnessing Animal Power
Animal manure, when properly composted, is an excellent source of organic fertilizer. It provides essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, along with organic matter. However, it’s crucial to ensure that the manure is fully composted to avoid the risk of pathogens and weed seeds. Different types of manure, such as cow, horse, and poultry, offer varying nutrient profiles and can be tailored to specific plant needs. Pictured below is one of the totes we bring in each year from a high-quality supplier. This is composted pelleted chicken manure. It also contains a small amount of feathers that slowly release Nitrogen.
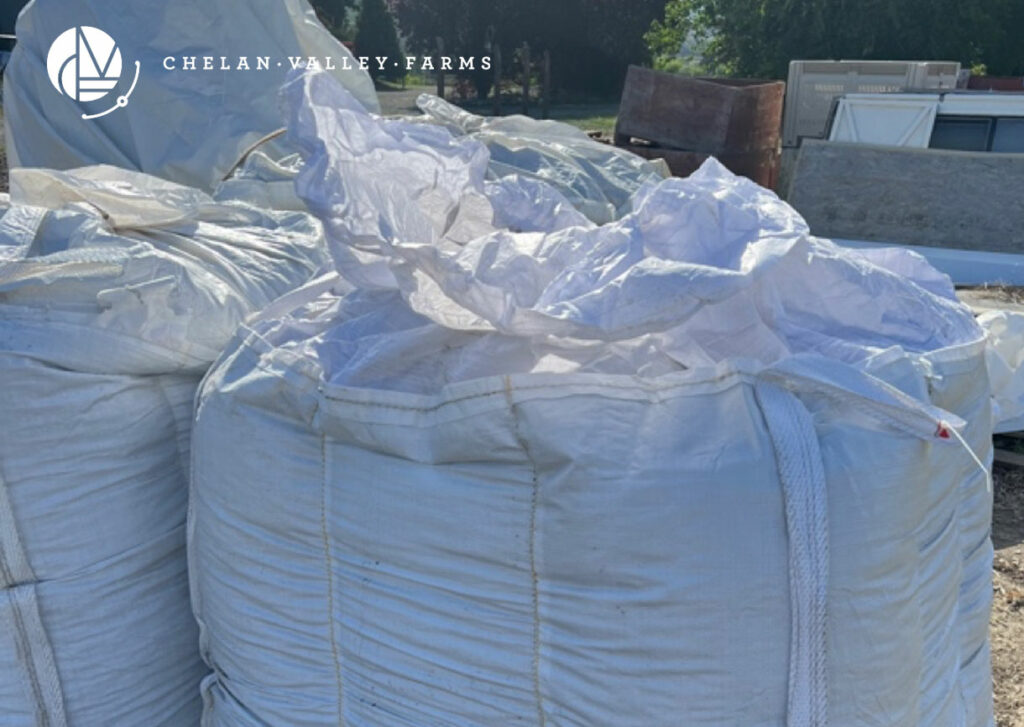
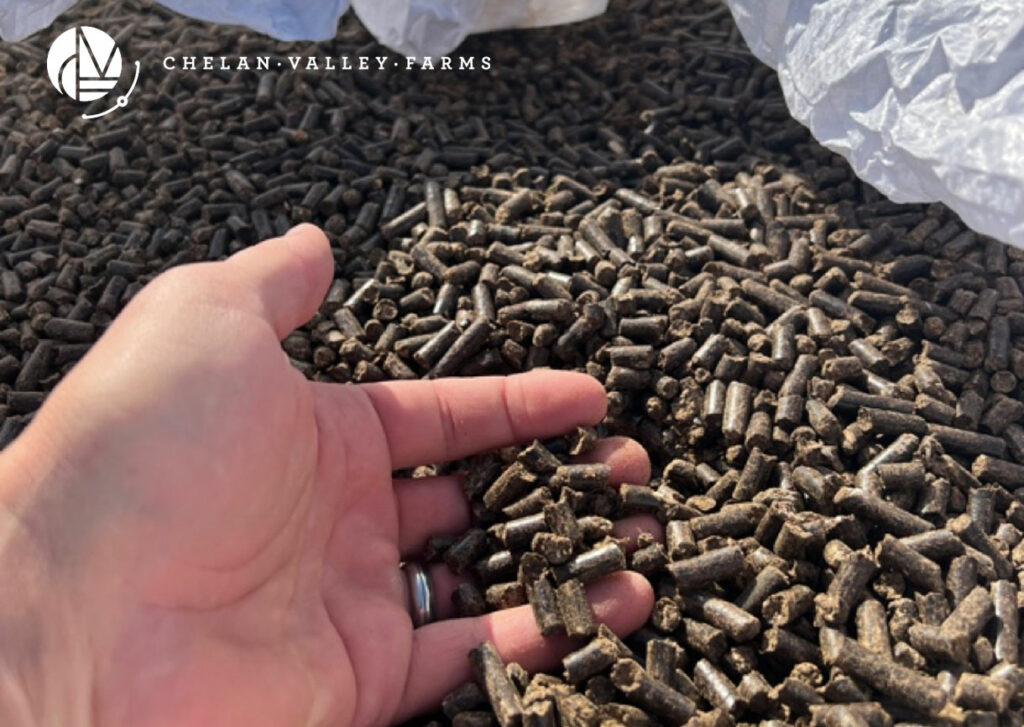


Green Manure: Cover and Nourish
Green manure refers to the practice of growing specific crops to be tilled back into the soil as a natural fertilizer. Legumes like clover and alfalfa are popular choices due to their ability to fix nitrogen from the atmosphere. The benefits of green manure include soil erosion prevention, improved soil structure, increased organic matter content, and nutrient enrichment.
Organic Liquid Fertilizers: Nutrients on Tap
Liquid fertilizers provide a quick and easily absorbable source of nutrients for plants. They can be derived from various organic sources such as seaweed, fish emulsion, or compost tea. Liquid fertilizers are particularly useful for foliar feeding or for providing a boost during critical growth stages. They offer convenience and versatility, allowing for precise nutrient application.
The Importance of Soil Testing:
While organic fertilizers offer numerous benefits, it is essential to understand the unique needs of your soil. Conducting a soil test is a vital step in determining the fertility levels and nutrient imbalances present in your garden or farm. Soil testing helps identify deficiencies or excesses of specific nutrients, enabling you to tailor your organic fertilizer choices accordingly. By addressing nutrient imbalances, you can optimize plant health, increase yields, and minimize environmental impact.
Conclusion:
Organic fertilizers provide a sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to nurturing our home gardens and small farms. Whether it’s compost, vermicompost, manure, green manure, or liquid fertilizers, each option has its distinct advantages. Remember to assess your soil’s fertility levels through soil testing, as it serves as the foundation for making informed fertilizer decisions. By embracing organic fertilizers and adopting soil testing practices, we can cultivate thriving gardens and contribute to a greener, healthier planet.
Happy gardening! Chad




So interesting!!